For super user across account there is a way to run raw read only SQL queries at the /explore/ page : https://iaso.bluesquare.org/explore/
e.g SELECT name FROM iaso_orgunittype
This is useful to check the database state and query data accross different client account. You can also save query and share them with others.
This feature is implemented via the excellent Django SQL Dashboard, their documentation has more complete information: https://django-sql-dashboard.datasette.io/en/stable/index.html
Tips#
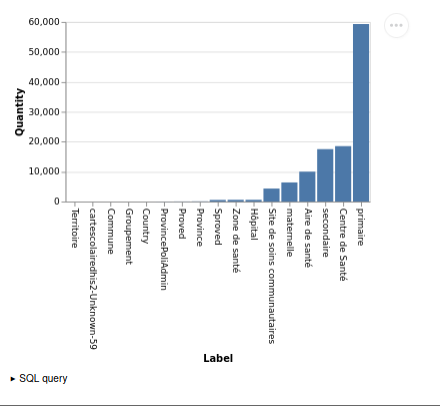
Bar charts#
You can generate bar chart by having two column named bar_label and bar_quantity
Examples
Example: Number of Org Unit per type in a project#
select iaso_orgunittype.name as bar_label, count(org_unit.id) as bar_quantity
from iaso_orgunittype
join iaso_orgunittype_projects on iaso_orgunittype.id = iaso_orgunittype_projects.orgunittype_id
left join iaso_orgunit org_unit on iaso_orgunittype.id = org_unit.org_unit_type_id
where iaso_orgunittype_projects.project_id = 1
group by iaso_orgunittype.id
order by bar_quantity
OrgUnit hierarchy linked to an org unit#
SELECT * FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*'
Use of parameters#
You can use parameter, this will automatically create an input.
If you save them as a dashboard it will allow passing the paramter in the url
Example number of submission per form and per org_unit in a particular SourceVersion (version_id)#
SELECT "iaso_orgunit"."path",
"iaso_orgunit"."name",
"iaso_instance"."form_id",
count("iaso_instance"."id") filter
(WHERE (not ("iaso_instance"."file" = '' and "iaso_instance"."file" is not null) and
not ("iaso_instance"."deleted" and "iaso_instance"."deleted" is not null))) as "instances_count"
FROM "iaso_orgunit"
JOIN "iaso_instance"
ON ("iaso_orgunit"."id" = "iaso_instance"."org_unit_id")
and version_id = %(version_id)s
GROUP BY "iaso_orgunit".path, "iaso_orgunit"."id", "iaso_instance"."form_id"
order by "iaso_orgunit".path
limit 100;
Use multiple ids#
This tips is useful to allow passing multiple ids, separated per ,
select * from iaso_form where
iaso_form.id = ANY (string_to_array(%(form_ids)s::text, ',')::int[])
Multi Line chart#
You can generate multi line chart by naming columns line_label, line_quantity and line_category (you need all three)
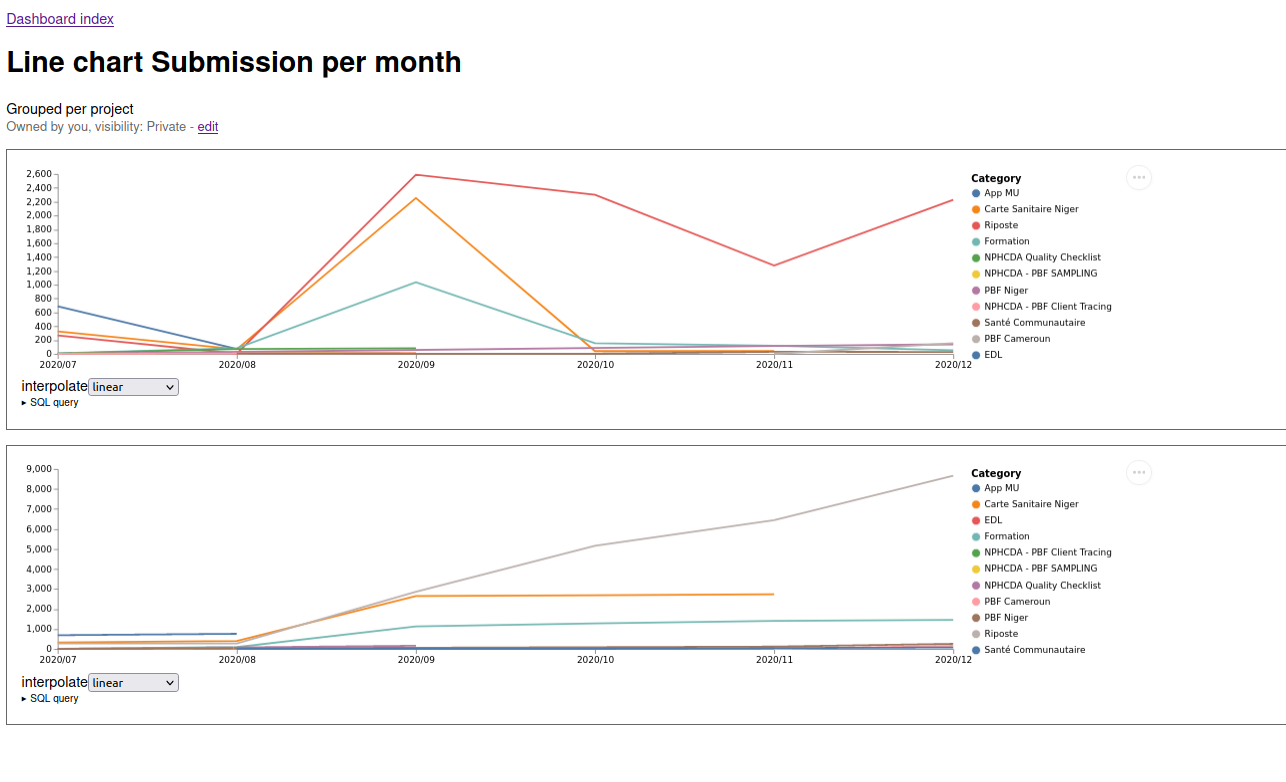
Example cumulative submission per projects per month#
select line_label,
line_category,
sum(line_quantity) over (PARTITION BY line_category order by line_label) as line_quantity
from (
select TO_CHAR(date_trunc('month', COALESCE(iaso_instance.source_created_at, iaso_instance.created_at)), 'YYYY/MM') as line_label, count(*) as line_quantity, iaso_project.name as line_category from iaso_instance inner join iaso_project on iaso_instance.project_id = iaso_project.id
group by line_label, iaso_project.name order by line_label, line_quantity desc limit 200
) as data
Cumulative sum#
To generate a cumulative sum (particularly useful for progression over time). Wrap your query with
select line_label,
line_category,
sum(line_quantity) over (PARTITION BY line_category order by line_label) as line_quantity
from (
YOUR QUERY
) as data
See previous example.
random data generation example#
select line_label,
line_category,
sum(line_quantity) over (PARTITION BY line_category order by line_label) as line_quantity
from (select TO_CHAR(gen_date.generate_series, 'YYYY/MM') as line_label,
(random() - 0.2) * 1000::int as line_quantity,
name as line_category
from (select *
from generate_series('2008-03-01 08:00'::timestamp,
'2009-03-04 12:00'::timestamp, '1 month')) gen_date
cross join (VALUES ('foo'), ('bar'), ('baz')) as categories (name)) as data
Searching in Org Units, Org Unit Types#
Here are some examples of queries to find Org Units, their types, reference forms and everything linked to the hierarchy of a specific Org Unit.
As we are using Postgre's ltree extension and django-ltree to model this hierarchy, specific SQL operators are available to search in a performant way and queries can be cumbersome.
Let's say you have a OrgUnit with ID : XXXXXX
Find the hierarchy linked to this Org Unit.#
SELECT * FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.XXXXXX.*'
Find the related Org Unit Types :#
SELECT * FROM iaso_orgunittype WHERE id IN
(SELECT org_unit_type_id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.XXXXXX.*')
Reference forms of these Org Unit Types#
SELECT * FROM iaso_form WHERE id IN
(SELECT reference_form_id FROM iaso_orgunittype WHERE id IN
(SELECT org_unit_type_id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.XXXXXX.*'))
Find the Form Versions of these Reference Forms.#
SELECT * FROM iaso_formversion WHERE id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_form WHERE id IN
(SELECT reference_form_id FROM iaso_orgunittype WHERE id IN
(SELECT org_unit_type_id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.XXXXXX.*')))
The Instances linked to that hierarchy#
SELECT * FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*')
Finding the projects linked to that hierarchy#
SELECT * FROM iaso_project WHERE id in
(SELECT project_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*'))
Devices linked to that hierarchy#
SELECT * FROM iaso_device WHERE id in
(SELECT device_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*'))
Accounts linked to these projects#
SELECT * FROM iaso_account WHERE id IN
(SELECT account_id FROM iaso_project WHERE id in
(SELECT project_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*')))
Source versions linked to these projects#
SELECT * FROM iaso_sourceversion WHERE id IN
(SELECT default_version_id FROM iaso_account WHERE id IN
(SELECT account_id FROM iaso_project WHERE id in
(SELECT project_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*'))))
Datasources linked to these versions#
SELECT * FROM iaso_datasource WHERE id IN (SELECT data_source_id FROM iaso_sourceversion WHERE id IN
(SELECT default_version_id FROM iaso_account WHERE id IN
(SELECT account_id FROM iaso_project WHERE id in
(SELECT project_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*')))))
Credentials linked these datasources#
SELECT * FROM iaso_externalcredentials WHERE id IN (SELECT credentials_id FROM iaso_datasource WHERE id IN (SELECT data_source_id FROM iaso_sourceversion WHERE id IN
(SELECT default_version_id FROM iaso_account WHERE id IN
(SELECT account_id FROM iaso_project WHERE id in
(SELECT project_id FROM iaso_instance WHERE org_unit_id IN
(SELECT id FROM iaso_orgunit WHERE path ~ '*.104133.*'))))))
Restrictions#
This functionality is severly restricted to prevent the risk of data leak and security issues:
- Only a certain set of table are accessible. (notably not the user table password)
- Since this is ignore the multi tenant rule only super user can be given access to it
- Access is read only (see implementation detail)
Configuration and Implementation detail#
To garantee read only access this feature use a separate user that should only be given restricted right.
The functionnality is automatically enabled if this user is set via the DB_READONLY_USERNAME environment variable.
To configure it:
Create a Postgresql user with a password and no acess and give him the role readonlyrole.
You can do so using the sql command
GRANT readonlyrole to YOUR_USER
Set the environment variable DB_READONLY_USERNAME and DB_READONLY_PASSWORD.
Some migration will give read acess to the certain tables to the readonlyrole, should you give access to more table use the command
GRANT SELECT ON TABLE
iaso_new_table_1,
iaso_new_table_2,
TO "readonlyrole";
to only give access to certain column on a table
GRANT SELECT(
id, username, is_active, date_joined
) ON auth_user TO "readonlyrole";
See also https://django-sql-dashboard.datasette.io/en/stable/security.html
In local dev#
this feature is automatically enabled.